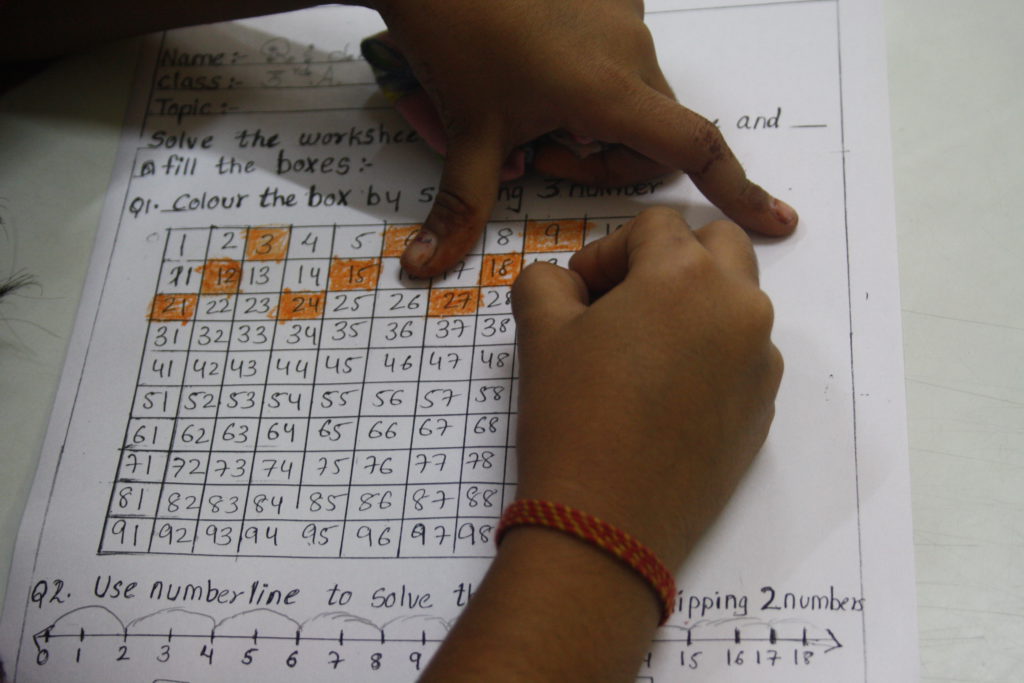
This report presents the results of RTI International Education’s study on teachers’ guides across 13 countries and 19 projects. Using quantitative and qualitative methods, the report examines how teachers’ guides across the projects differ and find substantial variation in the design and structure of the documents.